Internal Linking on WordPress: All You Need to Know!
Internal linking is the bottleneck of content writing; it costs a lot of time and is task-intensive.
In this complete guide to internal linking on WordPress, we’ll cover all the key points:
- What is internal linking?
- Why are internal links important?
- What makes up an internal link?
- Types of internal links
- Internal Links vs. External Links
- How to add internal links in WordPress
- How to change internal links in WordPress
- Internal linking SEO best practices
- Internal linking automation
What Is Internal Linking?
Internal linking is the act of creating hyperlinks on WordPress that lead to certain pages or posts on a particular website. It is simply the process of connecting internal pages to provide more information to users and search engines as a whole.
Internal linking, they say, involves a lot of daunting processes—from finding internal linking opportunities to visiting older content after a new post is released, etc., which are just what you must pass through for a good internal linking structure.
What Is an Internal Link and Why Is It Important?
An internal link results from interlinking your content. It’s created through the process of internal link building.
Simply, an internal link is a hyperlink that leads to other parts of a website. There’s only one rule — the link must stay within the site (i.e., it shouldn’t point to other websites) for it to be an internal link.
Why Are Internal Links Important?
Adding internal links in WordPress comes with a lot of benefits, ranging from the user’s end to the search bots that do the crawling and indexing work.
1. Benefits Visitors
Internal links allow users to discover more of your content, thereby increasing dwell time. Visitors get to visit your related pages to gain knowledge since a page can’t contain everything.
2. Helps Search Engine Bots
Internal links help search engine bots to a great extent by allowing them to discover more URLs to crawl. A properly done internal linking strategy can promote easier indexability on SERPs.
3. Matters to SEO
Given the recent leak on Google ranking factors, which exposed algorithms like NavBoost, internal linking has become more vital because it’s the master key when it comes to engaging users for a long dwell time, which improves SEO.
Many case studies around the act of internal linking have proven that it does matter to SEO.
Having more of it helps your E-E-A-T (a search quality guideline used by Google), which can indirectly influence the ranking of your website.
More internal links create a well-rounded experience around a specific subject.
Note: E-E-A-T stands for Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness.
4. Passes Link Equity
Internal links pass link power, called link equity or link juice.
Every page of a site has its own page authority. The authority is mostly determined by the quality of backlinks pointing to the page.
Internal links carry this authority across other pages of your site.
The closer an internal link is to the top of a page, the higher the link juice it passes. The fewer internal links on a page, the higher the link juice each link passes.
Link juice is shared among all the internal links in a given content.
What Makes Up an Internal Link?
An internal link is made up of two parts — an anchor text and a URL.
The anchor is a covering in the form of a text that disguises the URL. The URL is the page or post on the website where a user lands after clicking the hyperlink.
The combination of a URL and an anchor text forms an internal link (or a hyperlink).
Types of Internal Links
There are many types of internal links. Here are some of them:
- Navigational Links – Found in menus, sidebars, and footers, helping users move through the site easily. Example: The main navigation menu linking to key pages.
- Contextual Links – Placed within the content, guiding users to related articles or important resources. They also pass SEO value to the linked pages.
- Breadcrumb Links – Show a user’s path within a website, helping with navigation and SEO. Example: Home > Category > Post Title.
- Footer Links – Found at the bottom of a website, usually linking to legal pages, contact pages, or other essential resources.
- Sidebar Links – Appear in the sidebar of a webpage, often showing related posts, categories, or recent content.
- Related Post Links – Suggest additional content at the end of an article, encouraging users to continue reading.
- Category and Tag Links – Link to archive pages that list posts under a specific category or tag, improving content discoverability.
- Image Links – Clickable images that serve as internal links, directing users to another page within the site.
- Table of Contents (TOC) Links – Allow users to jump to specific sections of a long article, improving readability and navigation.
Each type of internal link plays a role in user experience, SEO, and content organization.
—
Internal links can also be categorized into Inbound Internal Links and Outbound Internal Links for proper internal link analysis.
Inbound Internal Links are simply links from other pages of your site. They’re the most important type of internal link.
Reason being—they push something called link juice (transmitted through hyperlinking) to the linked page.
Outbound Internal Links, on the other hand, are the internal links you add as you work on WordPress. They point to other pages on your site, giving them relative authority.
Internal Links vs. External Links
Internal links and external links serve different purposes in website navigation and SEO.
Internal links connect one page of a website to another page within the same domain. They help users navigate the site, improve SEO by distributing link authority, and enhance content discoverability.
External links point to a different website or domain. These links provide additional resources, boost credibility by referencing authoritative sources, and can help with SEO when used strategically.
While internal links strengthen a website’s structure, external links build connections with other sites. Both are essential for a well-optimized WordPress website.
How to Add Internal Links in WordPress
Adding an internal link on WordPress is a no-brainer.
To add an internal link—visit the desired page and locate the area (usually a text) where you want the hyperlink to appear.
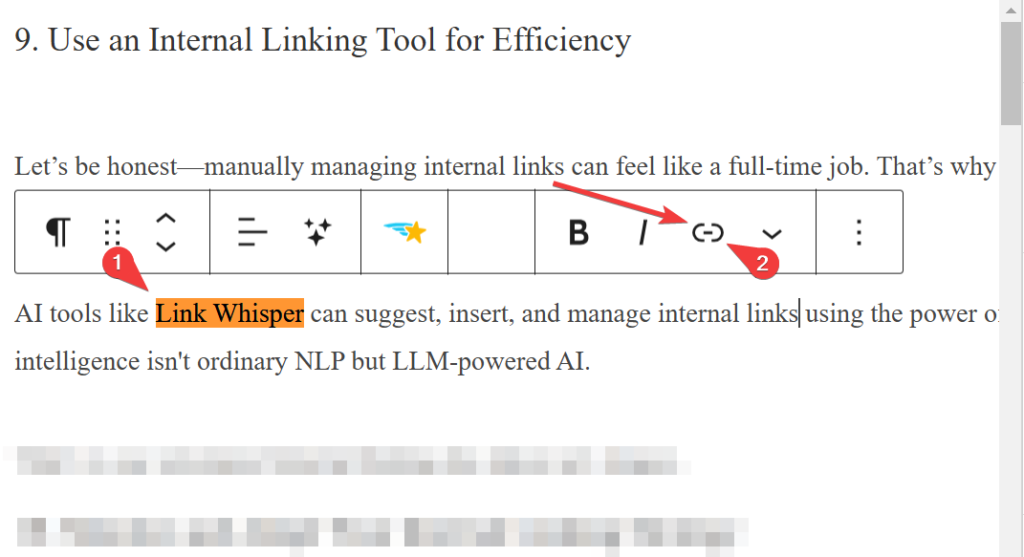
Upon finding it, highlight the text, select the link icon, and then search your site for the page you want to interlink. Alternatively, you can paste or type in the URL if it’s copied or known.
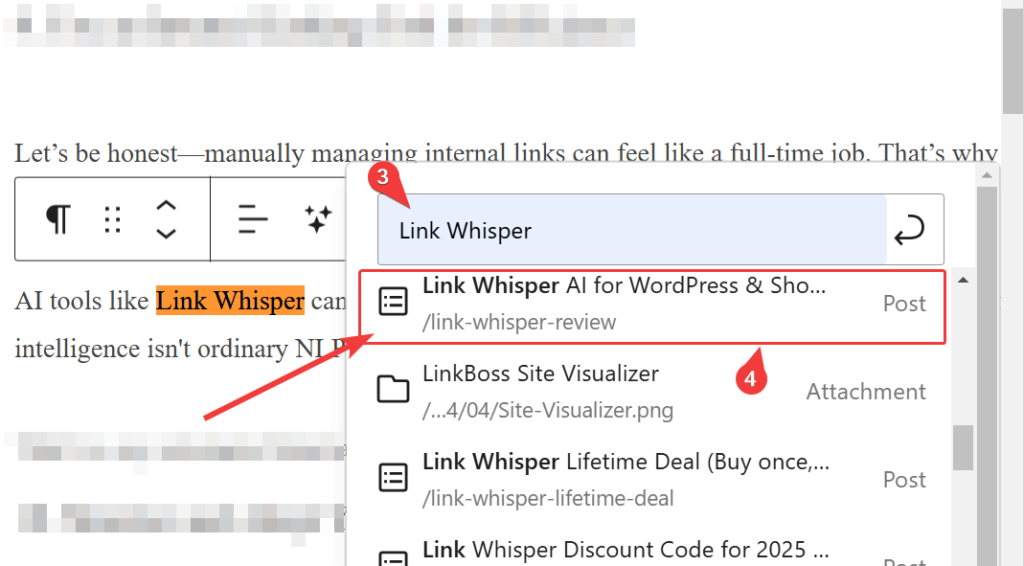
Then use the Enter button to apply the link to the text, thereby making an internal link.
There’s an option to configure the link attribute and behavior settings after adding a link.
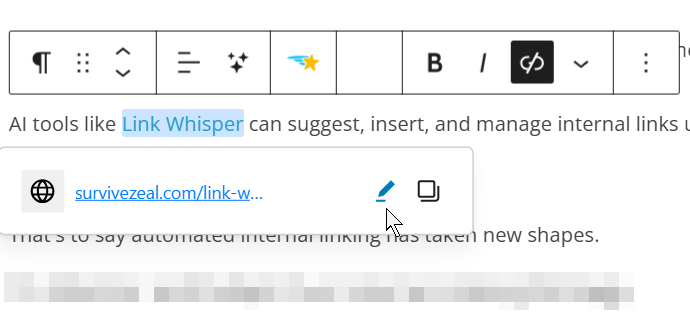
To access it, select the created link, then click the pencil icon.
Here you can see the following:
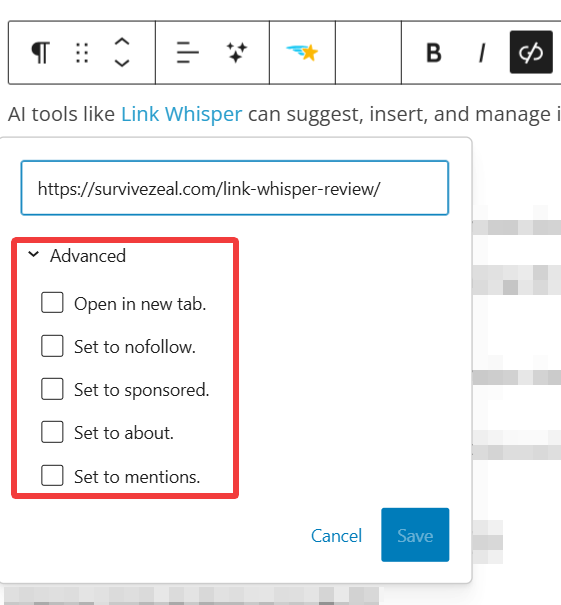
- Open in new tab: Not recommended for internal links, as it can overwhelm users.
- Set to nofollow: Used for external links to prevent passing link juice.
- Set to sponsored: For affiliate or paid links—not recommended for internal links.
- Set to about: Rarely used, except for “About” pages.
- Set to mentions: Used when referencing an entity—more relevant for external links.
Since we’re building internal links, none of these settings matter.
Note: You can add internal links automatically using Link Whisper.
How to Change Internal Links on WordPress
Changing internal links on WordPress is almost the same as adding them.
The only difference here is—you merely have to locate the created link, then replace the link it already has. Done and dusted.
Internal Linking SEO Best Practices
Now that we have learned how to create and change internal links on WordPress, let’s talk about SEO best practices for internal linking on WordPress.
It will greatly assist in building relevant and high-quality links that are beneficial to site visitors and search engine crawlers.
Best Internal Linking Practices
To harness the power of internal linking on WordPress, follow these best practices:
- Build a Content Hub – Organize related topics into pillar pages and cluster pages to improve site authority, navigation, and SEO.
- Transfer Link Authority – Pass link equity from high-authority pages to important ones by linking strategically.
- Prioritize Important Links – Place key internal links early in your content and use optimized, natural anchor text.
- Focus on Relevance Over Quantity – Avoid excessive links; instead, ensure each internal link provides real value.
- Use Proper Link Attributes – Internal links should be dofollow, while external links may use nofollow, sponsored, or UGC tags when necessary.
- Vary Anchor Texts – Prevent keyword cannibalization by diversifying anchor text for different pages.
- Update Internal Links Regularly – Add links to new content and fix broken or orphaned links to maintain a strong linking structure.
- Leverage Internal Linking Tools – Find internal linking opportunities automatically
For a detailed piece, check out our complete guide on best internal linking practices.
Internal Linking Automation

Just as internal links can be added manually, artificial intelligence can add them automatically.
Internal linking automation has grown beyond keyword-based linking, which SEOs previously criticized. Even now, keyword-based linking offers incredible flexibility, such as the ability to select links before adding them to your content.
The form of internal linking automation I prefer the most is semi-automation.
Semi-Automation Includes:
- Finding opportunities for internal links within a particular page
- Finding internal linking opportunities from older content
- Keyword-based linking with a preview ability
The second point prevents the need to manually visit older content for internal linking opportunities after adding a new post. AI runs this automatically for you, pulling suitable areas and allowing you to apply the ones you need.
You can learn more about adding internal links automatically on WordPress.
Conclusion
Internal linking is more than just placing hyperlinks across your site — it’s about building a well-connected network of content that enhances SEO and improves user experience.
With this article, I hope you now have a clear understanding of what internal linking is all about on the big CMS including how to conduct it.
Further reading will be – How to use internal links for SEO.
FAQs
Internal Links vs. External Links
Internal links connect pages within the same website. External links point to other websites.That’s the difference!
How Many Internal Links Per Page?
There’s no magic number, but quality over quantity is key. Link with context in mind — if it adds value, include it. Too many links can decrease link equity, which is the authority shared among every URL on a page.
How to Fix Broken Internal Links?
Simply use SEO tools or WordPress plugins to scan for broken links. Once found, either update the links, redirect them properly, or remove them altogether. Internal linking tools can also help you with that.
Benefits of Internal Linking
Internal linking has many benefits. It Improves user navigation, boosts SEO, passes link juice, and increases dwell time.
How to Find Internal Links to a Page?
You can simply find the internal links pointing to a specific page or the ones that are inside of it by running internal link analysis. Internal linking tools like Link Whisper can help you with that.

