Internal Linking for SEO: Best Practices and Strategies
Internal linking is the bottleneck of content writing; it costs a lot of time and is task-intensive.
In this complete guide on how to do internal linking for SEO, we’ll cover all these key points:
- What are internal links?
- Internal links vs. external links
- Internal links vs. backlinks
- Why are internal links important for SEO?
- How to build internal links for SEO
- Internal linking best practices
- Conclusion
What Are Internal Links?
Internal links are hyperlinks on a website that lead to other pages within the same website.
The main reason for internal links is to guide users to other content pieces related to a subject being discussed.
An internal link is made up of an anchor text and a URL.
The anchor text is the clickable text, usually colored, and is different from the text in the content. The URL bears the target page where the user will land after clicking the anchor text.
Internal links are different from external links and backlinks mainly from a location perspective. Here are the differences…
Internal Links vs. External Links
The main difference between internal links and external links is where they lead to.
Internal links lead to internal pages (i.e., pages of the same site), whereas external links lead to other websites.
Both help SEO — Internal links send signals to search engines about the structure of your content. External links, on the other hand, can be used by search engines to weigh the level of authority you have on a particular topic.
That’s why linking to authoritative sites is encouraged because Google and other search engines evaluate who you link to—to understand who you are.
Internal Links vs. Backlinks
Both internal links and backlinks have to do with your internal pages.
The real difference points to where the links are created — Internal links are created inside a website, whereas backlinks are created outside a website.
The internal pages are, of course, your various content pieces.
These internal pages, when linked within your site, lead to “internal links.” But when linked from other websites outside of your control, the result is “backlinks.”
Backlinks are links from other websites that lead to your internal pages. These links are of high value and help to encourage search engines to rank your content for a given query.
Internal links, let’s say, are a way to vouch for your own content. Backlinks, on the other hand, are a better way to do the vouching as they come from other people.
Both are needed for proper ranking on SERPs.
Why Are Internal Links Important for SEO?
Internal links are important from the perspective of SEO in so many ways.
In short, here are the benefits of internal linking for SEO:
- Guide users to relevant content on your site
- Increase dwell time and reduce bounce rate
- Guide search crawlers through the different content pieces on your site for indexing
- Pass link equity
1. Guide Users to Relevant Content on Your Site
The first benefit of internal linking is that it allows users to go through the various content related to a particular topic.
Internal links help users navigate all these pages, feeding them with the knowledge they need and also presenting you as an authority in their eyes.
2. Increases Dwell Time and Reduces Bounce Rate
As users follow internal links to discover subtopics and broader ones, the time they spend on-site increases.
Also, the rate of users leaving your site decreases (i.e., the bounce rate goes down). This is because users have many places to navigate besides hitting the “back” button.
So internal links do their job in helping you retain users for a longer time, decreasing bounce rate.
3. Guide Search Crawlers Through the Different Content Pieces on Your Site for Indexing
The benefit of internal linking extends beyond what the user gets. In addition to guiding users to different content, internal links also direct crawlers to your various pages.
This can increase the speed of indexing.
4. Passes Link Equity
When an internal link is created, there’s something called link equity or link juice that gets transferred to the target page.
Link equity is the value of authority that is distributed to all the links on a web page. It depends on the page’s authority and the quality of backlinks pointing to it.
Internal links make it possible to distribute the authority gained from backlinks to all other pages of your site, thereby leveraging that authority to boost search visibility.
How to Build Internal Links for SEO
Creating internal links is one thing, and optimizing them for SEO is another.
Internal link building is much more than pasting URLs into text. In order to follow a search-engine-optimized approach, you have to follow some best practices and set a strategy that guides you in all of it.
Setting Up an Internal Linking Strategy
An internal linking strategy is a mindset through which the act of interlinking is approached. It’s a set of rules for the internal linking work.
Creating an internal linking strategy starts with choosing the right architecture.
1. Find a Suitable Internal Linking Architecture
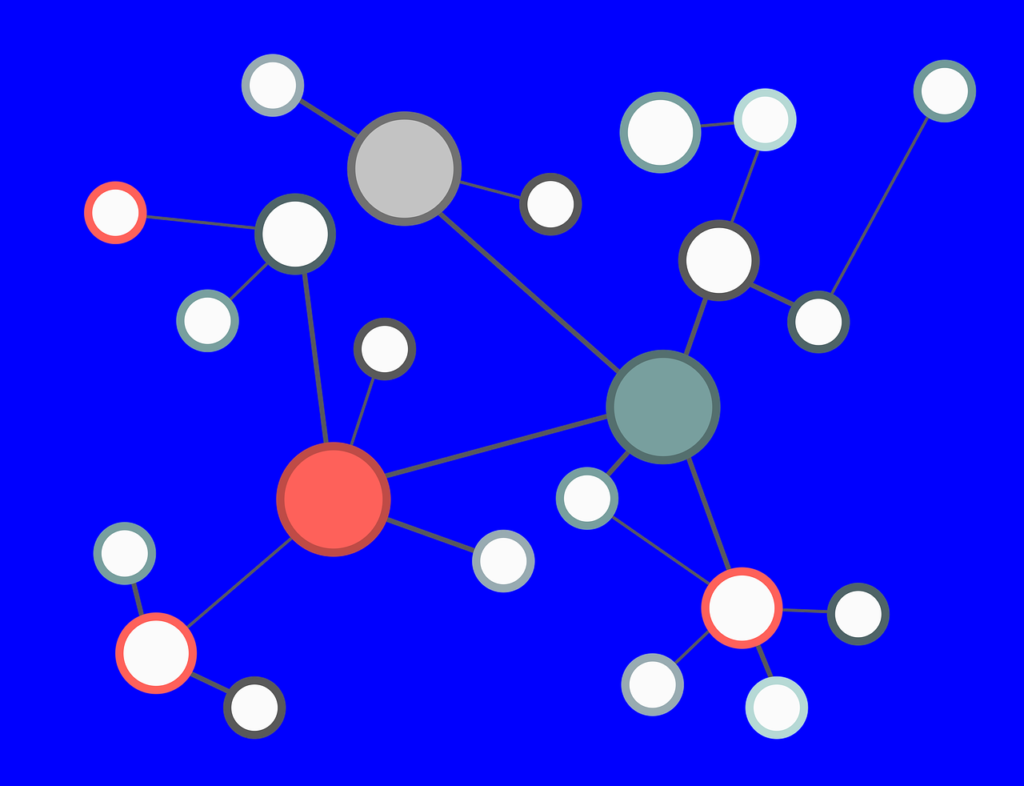
There are many internal linking architectures—Silos and content hubs are the most used.
A content hub is a type that involves the use of two elements—the Pillar pages and Clusters.
The Pillar pages are your cornerstone content focused on specific topics. They serve as a resource through which other related pages are discovered.
A pillar page broadly explores a topic while linking to related pages (the Clusters) that delve deeper into subtopics.
That’s what a content hub is all about.
Structuring your internal linking with this approach will establish you as an authority on that topic.
Your pillar pages should be your most important content. They should also have high search volume as well as potential for your business success.
I recommend Semrush’s guide to content hubs to educate you more on how to build one the right way.
For Silos, the same terms still apply. A silo is made up of a pillar page and Clusters.
In contrast to Content Hubs, Silos don’t permit linking to other Silos. That is to say, internal linking is restricted within the categories.
A Silo is simply a strict form of a content hub where pages that fall in a certain category/silo are not allowed to link to pages of a different category/silo.
You can also learn more about Silos and determine if one is the right choice for your business.
2. Link Pillar Pages and Clusters In-Between
After finding your pillar pages and their corresponding clusters, it’s time to link them in-between.
In your pillar pages, you should cover subtopics succinctly, then link to your clusters for detailed information.
Do the same for your cluster pages—point links back to the pillars at all times.
That’s an internal linking strategy that has to be maintained.
3. Repeat
After choosing an internal linking strategy that fits your site, it’s important to follow the process and not break it. Whether it’s a Silo setup or a Content Hub, the reward will surface gradually because as you make things easier for search engines and users, you’re also helping your site to rank better.
Then combine the work with the best internal linking practices below to make the most of it.
Internal Linking SEO Best Practices
The internal linking best practices here are a set of ways to perform the work and make the most of it. Following these guidelines will also ensure that you don’t harm yourself with the idea of helping your site.
1. Build a Content Hub and Expand It
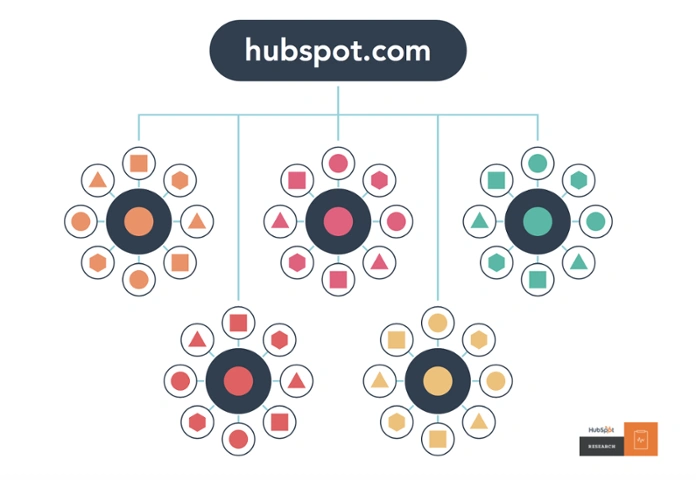
A content hub is a structured way of organizing related topics. It strengthens site authority, improves navigation, and enhances SEO. Google values well-organized sites, and internal linking plays a major role in making this happen.
A solid content hub consists of a pillar page (covering the main topic) and cluster pages (going deeper into subtopics). Internal links should connect these pages, making it easy for users and search engines to explore related content.
Regularly updating and expanding your content hub by adding new cluster pages keeps your site fresh and boosts visibility on SERPs.
2. Transfer Link Authority to Important Pages
Not all important pages naturally attract backlinks. That’s where internal linking comes in.
Find pages that have strong backlinks, then link from them to your key money pages. This way, you’re distributing link equity and helping search engines recognize the importance of those pages.
3. Prioritize Important Links and Use Optimized Anchors
Search engines prioritize the first few links on a page. That means your most critical internal links should appear early in your content.
Your anchor text also matters. Use keyword-rich anchors that make sense for both search engines and users.
Just don’t overdo it — Google frowns on excessive keyword stuffing. A natural mix, including LSI keywords, works best.
4. Focus on Contextual Linking Over Quantity
More links don’t always mean better SEO. In fact, stuffing a page with too many links can dilute link value and confuse users.
The fix? Keep your links contextually relevant. If a link doesn’t genuinely help users navigate your site or provide extra value, don’t add it.
5. Use Appropriate Link Attributes
Not all links are created equal. When linking to external sites, you need to control link equity by using the right attributes:
- nofollow: Stops search engines from passing authority to the linked site.
- sponsored: Used for affiliate and paid links to comply with Google’s guidelines.
- UGC (User-Generated Content): Best for comment sections and forum posts.
Using these correctly protects your site from SEO penalties while maintaining a clean linking structure.
The dofollow attribute should be used for internal links.
6. Avoid Using Identical Anchor Texts for Multiple Pages
Repeating the same anchor text across multiple pages confuses search engines. If Google sees multiple pages competing for the same keyword, it may not know which one to rank. This problem is called keyword cannibalization.
Solution? Vary your anchor texts so search engines can properly assign rankings and context to each page.
7. Regularly Update Internal Links
As your website grows, new pages will be added. If you don’t go back and add internal links to them, those pages could end up buried.
Find older, relevant pages and add links to newer ones. Yes, it takes time, but it’s worth it for SEO gains.
8. Fix Orphaned Content, Broken Links & 404 Errors
Orphaned content (pages with no internal link) is often ignored by search engines. That’s bad news for rankings.
Use SEO tools to find orphaned content and broken links. Fixing these ensures that all your pages are connected and fully indexed by Google.
9. Use an Internal Linking Tool for Efficiency
Let’s be honest—manually managing internal links can feel like a full-time job. That’s why internal linking tools have come to help us.
AI tools like Link Whisper can suggest, insert, and manage internal links using the power of AI. And the artificial intelligence isn’t ordinary NLP but LLM-powered AI.
That’s to say automated internal linking has taken new shapes.
10. Monitor and Adapt Your Internal Linking Strategy
SEO isn’t a set-and-forget process. You need to analyze, tweak, and optimize your internal links over time.
Use internal linking tools to track which links get clicks and adjust your strategy accordingly. The more strategic you are with internal linking, the better your SEO results.
More on Internal Linking for SEO
Internal Link Analysis and Audit
Performing an internal linking analysis will give you a bird’s-eye view of the structure of your internal links. It’s one of the boxes to tick when performing an internal linking audit for SEO.
An internal linking audit can be performed using different tools like Semrush, Ahrefs, and other SEO tools.
But the kind of analysis provided by internal linking tools goes beyond the basics. These tools go further by revealing not just the internal link counts for your pages but the actual hyperlinks that are present.
Internal linking analysis in interlinking tools fetches the following:
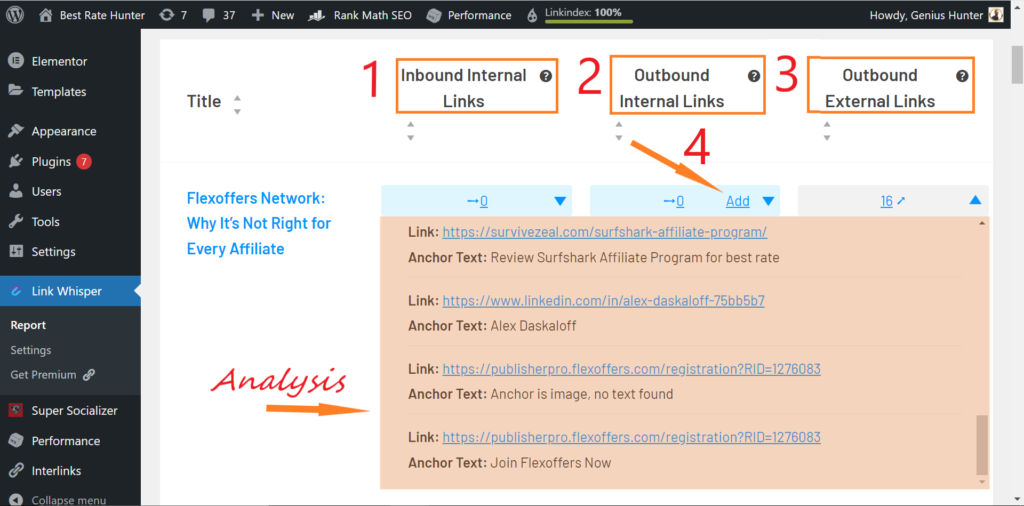
- The individual incoming internal links on each page
- The individual outgoing internal links on each page
- The anchor texts
- The naked URLs
Internal link analysis can be conducted in an engaging way—particularly through internal link visualization. Here, you get to see how your pages are interconnected.
Needless to say, the act of internal link auditing answers questions like how to find internal links pointing to or from a page.
Internal Linking Tools
Internal linking tools can go a long way in freeing the time the process takes. They achieve this in many ways —
- By finding internal linking opportunities within a page
- By finding internal linking opportunities from other pages
- By automating internal linking by keywords
Unlike before, when internal linking tools were avoided, they can now serve the same function as humans.
These tools can go through all your pages, finding opportunities for internal links. And you know what that means? — You no longer need to open older content after publishing new posts.
Moreover, internal linking tools help with critical analysis and reporting of your interlinking profile. And they can automate a lot of things too, if not fully automate the process.
With the emergence of LLMs like ChatGPT, internal link suggestion tools now output better results.
If you haven’t yet tested their power, you may be missing out on potential time savings.
Conclusion
While internal linking can prove time-consuming and stressful, it is not safe to avoid it, especially when it comes to SEO.
“Internal linking for SEO” aims to use the potential power of internal links to perform well on SERPs.
We learned all about internal linking and how to build it while following the best SEO guidelines. We also touched on internal linking tools and how they are no longer the same as before.
This information will help you take your internal linking to the next level.
Adopt the SEO internal linking guidelines and see the difference.
FAQs
Let’s answer some questions on the topic—internal linking for SEO.
How many internal links should I use per page?
There’s no magic number. Just link contextually, not excessively.
A number of 3-5 links on a page is ideal for SEO. It’s advisable to aim for at least one link for every 300 words.
Mind you, there’s still no magic number. Approach linking contextually and make sure you’re not linking to content that won’t contribute any value.
Should I no-follow internal links?
Under normal circumstances, internal links should be followed, unless you don’t want search engines to value the linked page.
What’s the point? — Yes, you can go ahead and no-follow your internal link if the linked page isn’t worthy of appearing on SERPs for any reason.
What are the SEO benefits of having internal links in the footer?
When you have a link in the footer, technically, it will appear on every page of your site. That means all pages are linking to it.
There are many SEO benefits to attaching your valuable links in your footer. It can help your pages rank better and establish you as an authority on the topic.