10 HCU Recovery Tips From Leaked Google Algorithm Data
If you have once tried to recover a website hit by HCU but failed, then here is an opportunity to try again with EXPOSS (confirmed information).
Google recently made a huge mistake resulting to the leak of their search algorithm data. This is a disaster to the big search engine.
But it is a win to SEOs and content creators at large.
In this article, we will focus on how you can take advantage of this leaked ranking systems to recover a site victimized by the Helpful Content Update.
Now that we have set the stage, let’s get started.
10 HCU Recovery Tips From Leaked Google Search Data
Here are 10 valuable information and tips that can help you revive your website from Helpful Content Update.
1. Don’t relinquish in improving Site Authority
If you have already given up building relevant backlinks for revival, then you have to reconsider your footsteps.
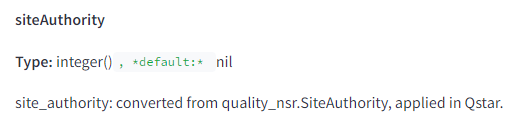
According to the leaked document, there is an attribute called “siteAuthority” which Google computes when ranking pages.
What does this mean? Nothing else than Google has been lying to us all this while.
The idea that Google considers overall authority when it comes to ranking Pages is so obvious.
If you go to the Search, you will see High DA websites capturing the top spots.
It does not matter whether a website with low authority has better content or not. The search engine behaves as if it has no other option than to give it the rank.
If you’re still having hard times recovering a site, don’t give up on building backlinks yet. You just have to know the right links to build.
2. Know the right links to build
Google follows a specific approach when it comes to indexing Pages.
The Search Engine would classify them into 3 tiers.

The first indexing tier uses flash memory for its storage and it packs content that is regularly updated and most important. The second tier uses SSD for its storage and it contains less important content. The last tier contains irregularly updated content and the storage system used here is HDD.
According to the leaked documentation, indexing tier impacts Link value.
What this mean in reality, is that — Backlinks from important Pages of a website would perform well than Backlinks from its less priority Pages.
Also, links from frequently updated content would outperform ones that are created from regions that have been forgotten or where attention is not given.
The SegIndexer is responsible for placing content into tiers.
That said, the next time you’ll try to acquire backlink, please target the most important Pages and also ensure that they are updated how they should.
This can mean – Guest blogging isn’t effective to take an impactful Link power from an authoritative website. This is because, Guest posting is mostly done once and the website owner is to decide whether your post should get updated or not.
Link insertion is powerful than Guest Post. That will be the interpretation.
I advise you only opt for Guest post if the website owner will give you Editing permission. This way, you can easily jump on a Page you’ve submitted for years and edit it to meet recent updates.
Let’s come again. Earn links from the ranking Pages of a website and fight for Editing permission if you must go with Guest posting.
It’s not always about building Links. You should learn how to play your game at a rate that won’t jeopardize your site.
3. Know the rate at which these right links should be built
You can potentially recover a site from Helpful Content Update with relevant backlinks.
Google has what they call “Link Spam Velocity Signals”. These hunt sites that build backlinks with intentions other than to increase visibility.
You should come up with a consistent link-building strategy and stick to it. Don’t overdo it because Google’s so-called Cookbooks will find you out right away.
The best course of action is to first check the rate at which you earn backlinks. Then, consider it as you take your site from the HCU disaster.
4. Maintain Content freshness

Just like we have said about how Google classifies her index into tiers following the rate of update, you should ensure that your content is fresh and up-to-date at all times.
Google uses re-ranking systems called Twiddlers to adjust the content of the SERP before finally displaying it to end users.
The system that checks for content freshness is called FreshnessTwiddler.
As you might have experienced, a Page tends to lose in ranking as it ages overtime.
This is the work of the FreshnessTwiddler.
Google is always working to deliver results that are up-to-date. So it developed these methods to alter the SERP for freshness before it’s displayed to searchers.
If you have outdated content on your site, try to update them with immediate effect. It will help all-round.
5. Pursue Long clicks to your Pages
If your site got demoted after the HCU Update, you may try to monitor the overall user experience and movement on your site.
If you have lots of thin content, it will negatively impact Long clicks to your Pages.
We are still talking about Twiddlers, Google’s system that filters search result by internal metrics.
The specific one being talked about here is NavBoost.
According to the Compressed Quality Signal (i.e, the Leaked Data), the big Search Engine tracks and re-ranks web Pages overtime according to their clicks performance on SERPs.
NavBoost basically computes clicks to web pages that make up a given search result. After getting click information, the system subsequently use it to adjust individual page ranks.

NavBoost checks the following:
- Bad clicks: This indicates clicks to a Page that are horrendous. e.g. Searcher clicks on a result and immediately bounces back, Searcher clicks on a result and didn’t spend a good amount of time before leaving the Page.
- Good clicks: This indicates clicks that are positive and have yielded positive user experience. e.g. Searcher opened a page and spent a good amount of time on it, Searcher clicked to more Pages of the site as he reviews a Page.
- Last longest clicks: Used to measure the time users spend on a page.
- Unsquashed clicks: This indicates clicks that are genuine and valuable.
- Squashed clicks: This indicates spam clicks and ones of low value.
What we can learn from NavBoost is to optimize for not just clickthroughs but also for excellent user experience.
Therefore, a compelling title is good for a Page since it increases CTRs which in turn means better ranking.
If you’re observant, you have probably caught the boosting of Pages on SERPs with click-worthy titles.
A good balance between a click-whorthy title and a keyword-rich one should be maintained.
Note: Users are seen as voters by NavBoost and their clicks are stored. This reminds me of the Upvote ability on Product Hunt. When so many users are clicking to a Page, this would mean the Page is receiving significant upvotes which means higher Search position.
Now you got it!
It’s over to you to take another look on your click performance on SERPs.
Look out for titles that aren’t optimized for click-worthiness and make them catchy. Find Pages whose content don’t deliver good experience to readers and improve them.
You should take this tip seriously because NavBoost has been recognized as one of Google’s strongest ranking signals by many sources.
6. Come out of the Sandbox
If your site was showing up on Google but suddenly disappeared after the helpful content update, then this likely means you’re sandboxed.
Google is purposely hurting small personal sites obviously.

To add to this, there’s an attribute inside the Leaked Google Search Documentation called “small personal site”.
Why is such an attribute there? You can answer that question.
The big but now losing Search Engine has constantly denied the idea that they sandbox new websites and sites of low trust.
But the Leaked Data has exposed its existence.
There’s yet another attribute called “hostAge” which puts the age of sites in consideration.
Google will typically place new websites and sites of low trust scores in the sandbox until they build trust to theirselves.
If the Search Engine have found your site guilty of low trust, you can simply recover by staying consistent and acquiring links from trustworthy sites.
7. Understand Google Demotions and check if you’re a victim
It’s also a good idea to understand Google’s Demotions found inside the Leaked Search Data.
This can help you identify if you are likely a victim of a particular Demotion.
Here are what Google targets from websites before pulling the trigger of utter deindexation and position demotion.
- Anchor Mismatch: Occurs when the text used in hyperlinks (anchor text) is not relevant or consistent with the content of the linked page.
- SERP Demotion: A general decrease in ranking within the search engine results pages (SERPs) due to various quality or relevancy issues.
- Nav Demotion: Related to the navigation structure of a website. Poor or confusing navigation can lead to demotion.
- Exact Match Domains Demotion: Penalizes domains that exactly match popular search terms but do not provide high-quality content.
- Product Review Demotion: Affects sites with low-quality or biased product reviews, often aimed at those with affiliate links or sponsored content that lack genuine insight.
- Location Demotion: Targeted at sites that do not provide relevant local content or have misleading location-based information.
- Porn Demotion: Applies to sites containing adult content that is not appropriate for general search results.
- Ad-heavy Demotion: Sites with too many ads above the fold, affecting user experience and readability.
- Content Quality Demotion: Affects sites with thin, duplicate, or low-quality content that doesn’t provide value to users.
- Speed Demotion: Sites with slow loading times can be demoted as they negatively impact user experience.
- Mobile Usability Demotion: Sites that are not optimized for mobile devices can be penalized, affecting their mobile search rankings.
- Keyword Stuffing Demotion: Penalizes sites that use an excessive amount of keywords in an attempt to manipulate search rankings.
- User Engagement Demotion: Sites with poor user engagement metrics (high bounce rate, low time on site) can be demoted.
- Security Demotion: Sites that lack proper security measures (e.g., HTTPS) or have been compromised can be penalized.
- Manual Actions: Direct penalties from Google’s webspam team for violating guidelines, such as using black-hat SEO techniques.
- Cloaking Demotion: Penalizes sites that show different content to users than to search engines, a deceptive practice to manipulate rankings.
If you ticked any of the box, you don’t have any other option than to go and fix things up.
8. Find and fix thin content
We are still on the same talk of Content Quality Demotion.
Thin content are Pages with little to no added value. In reality, they don’t give anything new to the user.
It’s mostly a very short piece of content that is lazily created. Long content that is filled with jargons and unhelpful information also fall in the same category.
I think Google sends pings from GSC whenever it rules off thin content from its engine.
In order to survive a site after Helpful Content Update, you should ensure that thin content are edited to include valuable information. If you don’t want to edit the pages, you can simply remove them.
Don’t let thin content hold you back.
9. Ascertain if you’re actually hit by HCU or Core Update

Well, I have a site that was actually hit by the Core Update. I mistook it for the HCU Update.
And all these while, I have been circling around the same problem.
That site only came back to life when I understood that the HCU Update wasn’t my problem.
I simply built few backlinks and you know what, it appears on Google search result again.
That site was literally beneath a “siteAuthority” score ideal for webpages to adapt after SERP adjustments.
10. Patiently wait for optimistic result
After applying all these methods, keep repeating them and continue producing valuable content.
And most importantly, be optimistic and wait for your site’s revival.
Conclusion
Getting a site back to its initial spot after the HCU Update can look overwhelming.
But thankfully, we now have Google’s Search Ranking Signals on hand. And these would better our odds.
FYI, Google has confirmed that the Leaked Search Data is realistic. Check here.
That is to say, we are not speaking out of assumptions, we are conveying information that is proven to work.
Let’s refresh the memory.
“We don’t have to faint when it comes to building backlinks,” says an attribute called siteAuthority from the Leaked Data.
We only have to ascertain the best place to build backlinks from. Ranking/important Pages of an authoritative website is our target.
We also have to follow a steady Backlink acquisition so that the Link Spam Velocity signals won’t find us out.
Importantly, we should maintain Content freshness because reranking systems like the FreshnessTwiddlers alters SERP content for latest information.
Attracting not just Clicks but Engagement to our Pages is a game we don’t want to lose. We have learnt that maintaining a balance between Catchy Title tag and Keyword-rich one would yield better result.
Getting hit out completely from Google Search Result is the same as being sandboxed. We can employ several tactics to come out of it.
We can also look out for potential Google’s Demotions triggers to discover if we are victim of one. The day you discover is actually the day you’ll recover.
Last but not the least, we noticed a very clear message that says – Ascertain if you’re actually hit by HCU or Core Update.
That’s no joke. Because many folks are suffering from the Core Update and still they mistook it for the Helpful Content Update.
It was drilled into us that a Website whose Domain Authority is low (particularly below 10) can easily recover by building few relevant backlinks. Still the function of the Core Update here.
After we have applied the HCU Recovery Tips picked from the Leaked Google Search Data, it’s highly advisable that we anticipate the best for our sites.
Simply being consistent with producing valuable content and redoing the tactics over and over again, we can possibly resuscitate our site from the HCU sandbox.
If you wan to learn about the leaked Google Search Algorithm Data, check the masterpiece of Ipullranks.